Myopia
Advanced myopia management providing precise vision correction and proven strategies to slow progression, protect eye health, and maintain clear distance vision for the future.
Corneal Keratoconus Treatment
Discover effective treatments for corneal keratoconus, a condition affecting the cornea’s shape and clarity of vision. Our specialized approaches can help improve your eyesight and overall eye health. Learn more about the options available to manage and treat this condition.
What Is Myopia?
Myopia, also known as nearsightedness, is a common refractive error that occurs when the eyeball elongates, causing light to focus in front of the retina instead of directly on it. This optical misalignment results in blurred vision when looking at distant objects, while close objects remain clear and easy to see.
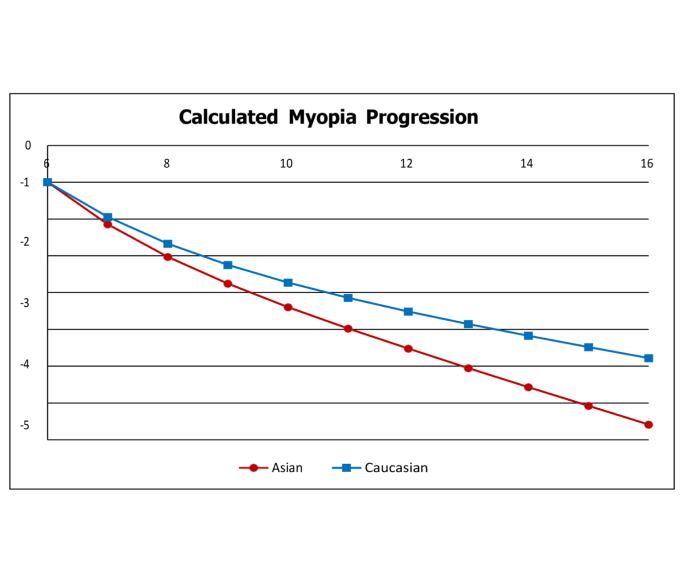
Myopia typically manifests during childhood, often first detected when a child begins school. As a child grows, the condition tends to progress, making regular vision checks essential for timely adjustments to corrective lenses. It’s important to note that myopia doesn’t follow a one-size-fits-all pattern; its progression can vary significantly among individuals. For many, the condition stabilizes in the late adolescent years, generally in the early 20s.
What Causes Myopia?
Myopia onset is multi-factorial: Heredity, Lifestyle & other Unknown factors
Heredity: Parental Myopia1
Two myopic parents: ~ 6x risk
One myopic parent: ~ 3x risk
~when compared to children with no myopic parents
What causes MYOPIA?

The Risks of Myopia
As myopia progresses with age, it could develop into high myopia (> -5.00D) by the time myopia stabilizes in the late teens
In high myopia (>5.00D), the excessive increase in axial length could lead to:
Thinning of tissues inside the eyes (retina and sclera)
Tearing of the retina
Degeneration at the macular
Resulting in pathological complications which could threaten vision, later on in life
Related Doctors
Consultant Ophthalmologist
Anterior Segment, Oculoplastic Surgeon & Pediatric Ophthalmology
Specialist Ophthalmologist
Head Of Pediatric Ophthalmology & Strabismus Unit
Customer Reviews
Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Eye Consultants provides specialised eye care services. Their facilities include consultation rooms, diagnostic equipment, and treatment areas designed to support comprehensive eye health.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. نتقدم بالشكر للدكتور احمد الخشاب وجميع الأطباء وجميع العاملين بالمركز على المعاملة الملاءكية من الجميعPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I did my procedure with Dr. Mahmoud and I am glad I came here. They were very supportive with each step and my procedure was done with great care. 100% recommended❤️Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. The experience was fantastic. The staffs are professionals and the Dr is very experience. Very good experience here.Posted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Very helpful and professional team Special thanks for Dr Ahmed Al KhashabPosted onTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. شكرا خاص لطافم العمل صراحه على المتابعه و الاحترام في التعامل صراحه بردوا بسرعه و متعاونين و شكرا خاص للدكتور لانه كان جدا محترم و شاطر و اسلوبه جميل بالشرح



